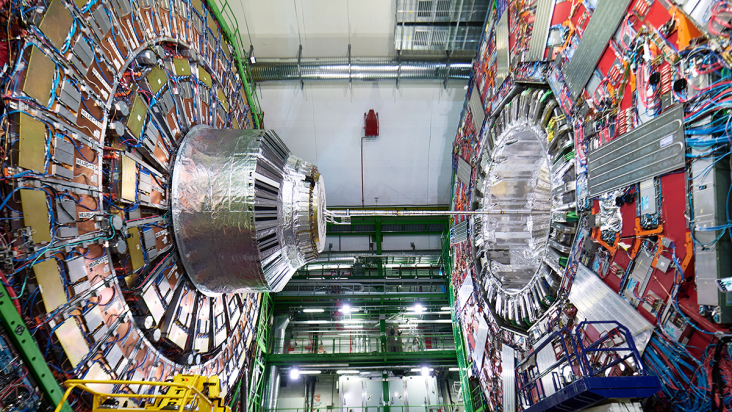
 Read article 'CMS observes top–antitop excess'
Read article 'CMS observes top–antitop excess'
 Read article 'CMS observes top–antitop excess'
Read article 'CMS observes top–antitop excess'
Vivian Poulin asks if the tension between a direct measurement of the Hubble constant and constraints from the early universe could be resolved by new physics.
With a new measurement imminent, the Courier explores the experimental results and theoretical calculations used to predict ‘muon g-2’ – one of particle physics’ mos...
Kurt Hinterbichler reviews Claudia de Rham's first-hand and personal glimpse into the life of a theoretical physicist and the process of discovery.
 Read about 'New-issue alert: sign up today'
Read about 'New-issue alert: sign up today'
Be the first to know when the new digital issue of CERN Courier is available to read by signing up to receive our new-issue alert
 Read article 'CDF addresses W-mass doubt'
Read article 'CDF addresses W-mass doubt'
Ongoing cross-checks at the Tevatron experiment reinforce its 2022 measurement of the mass of the W boson, which stands seven standard deviations above the Standard Model predictio...
 Read article 'Boost for compact fast radio bursts'
Read article 'Boost for compact fast radio bursts'
New results from the CHIME telescope support the hypothesis that fast radio bursts originate in close proximity to the turbulent magnetosphere of a central engine.
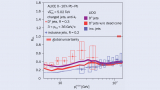 Read article 'Charm jets lose less energy'
Read article 'Charm jets lose less energy'
New results from the ALICE collaboration highlight the quark-mass and colour-charge dependence of energy loss in the quark-gluon plasma.
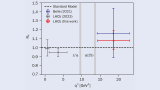 Read article 'Breaking new ground in flavour universality'
Read article 'Breaking new ground in flavour universality'
A new result from the LHCb collaboration further tightens constraints on the lepton-flavour-universality violation in rare B decays.
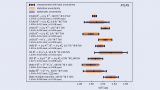 Read article 'A new record for precision on B-meson lifetimes'
Read article 'A new record for precision on B-meson lifetimes'
As direct searches for physics beyond the Standard Model continue to push frontiers at the LHC, the b-hadron physics sector remains a crucial source of insight for testing establis...
 Read article 'Isospin symmetry broken more than expected'
Read article 'Isospin symmetry broken more than expected'
The NA61/SHINE collaboration have observed a strikingly large imbalance between charged and neutral kaons in argon–scandium collisions.
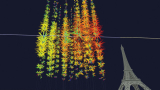 Read article 'Cosmogenic candidate lights up KM3NeT'
Read article 'Cosmogenic candidate lights up KM3NeT'
Strings of photodetectors anchored to the seabed off the coast of Sicily have detected the most energetic neutrino ever observed, smashing previous records.
 Read article 'Painting Higgs’ portrait in Paris'
Read article 'Painting Higgs’ portrait in Paris'
The 14th Higgs Hunting workshop deciphered the latest results from the ATLAS and CMS experiments.
 Read article 'Trial trap on a truck'
Read article 'Trial trap on a truck'
CERN'S BASE-STEP experiment has taken the first step in testing the world's most compact antimatter trap.
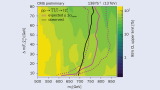 Read article 'Cornering compressed SUSY'
Read article 'Cornering compressed SUSY'
A new CMS analysis explores an often overlooked, difficult corner of SUSY manifestations: compressed sparticle mass spectra.
 Read article 'Chinese space station gears up for astrophysics'
Read article 'Chinese space station gears up for astrophysics'
China’s Tiangong space station represents one of the biggest projects in space exploration in recent decades.
 Read article 'Taking the lead in the monopole hunt'
Read article 'Taking the lead in the monopole hunt'
Magnetic monopoles are hypothetical particles that would carry magnetic charge, a concept first proposed by Paul Dirac in 1931.