Read article 'REX-ISOLDE accelerates the first isomeric beams'
Read article 'REX-ISOLDE accelerates the first isomeric beams'
REX-ISOLDE accelerates the first isomeric beams
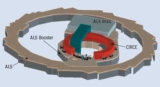
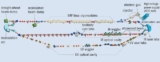
CERN's REX-ISOLDE facility has opened up a new avenue for nuclear investigations by accelerating isomeric beams for the first time, as Georgi Georgiev explains.