 Read article 'CMS looks into the dark'
Read article 'CMS looks into the dark'
CMS looks into the dark
If dark-QCD mediators were produced in pairs in the CMS detector, their signature would be striking.
Thank you for registering
If you'd like to change your details at any time, please visit My account
 Read article 'CMS looks into the dark'
Read article 'CMS looks into the dark'
If dark-QCD mediators were produced in pairs in the CMS detector, their signature would be striking.
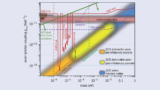 Read article 'Search for WISPs gains momentum'
Read article 'Search for WISPs gains momentum'
Interest is growing in new experiments that probe dark-matter candidates such as axions and other very weakly interacting sub-eV particles.
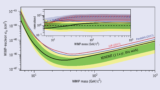 Read article 'Largest WIMP survey sets new limits'
Read article 'Largest WIMP survey sets new limits'
XENON1T is a 3D-imaging liquid-xenon time projection chamber located at Gran Sasso National Laboratory in Italy.
 Read article 'Study links solar activity to exotic dark matter'
Read article 'Study links solar activity to exotic dark matter'
The temporal distribution of solar flares is correlated with the positions of the Earth, Mercury and Venus.
 Read article 'CMS expands scope of dark-matter search in dijet channel'
Read article 'CMS expands scope of dark-matter search in dijet channel'
Using three complementary techniques, CMS has now explored a large range in mass, coupling and width.
 Read article 'XENON1T releases first data'
Read article 'XENON1T releases first data'
XENON1T is the first tonne-scale detector of its kind and is designed to search for WIMP dark matter by measuring nuclear recoils from WIMP–nucleus scattering.
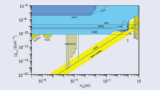 Read article 'CAST experiment constrains solar axions'
Read article 'CAST experiment constrains solar axions'
The CERN Axion Solar Telescope has reported important new exclusion limits on coupling of axions to photons.
 Read article 'Survey reveals edge of dark-matter halos'
Read article 'Survey reveals edge of dark-matter halos'
Results show that the density of dark matter in a halo does not gradually fall off with distance, as might be expected, but instead exhibits a sharp edge.
 Read article 'Dark-matter surprise in early universe'
Read article 'Dark-matter surprise in early universe'
A surprising result at the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics in Germany suggests that dark matter was less influential in the early universe than it is today.
 Read article 'Euclid to pinpoint nature of dark energy'
Read article 'Euclid to pinpoint nature of dark energy'
Due for launch in 2020, ESA’s Euclid probe will track galaxies and large areas of sky to find the cause of the cosmic acceleration.